🧬What is MOTS-c?
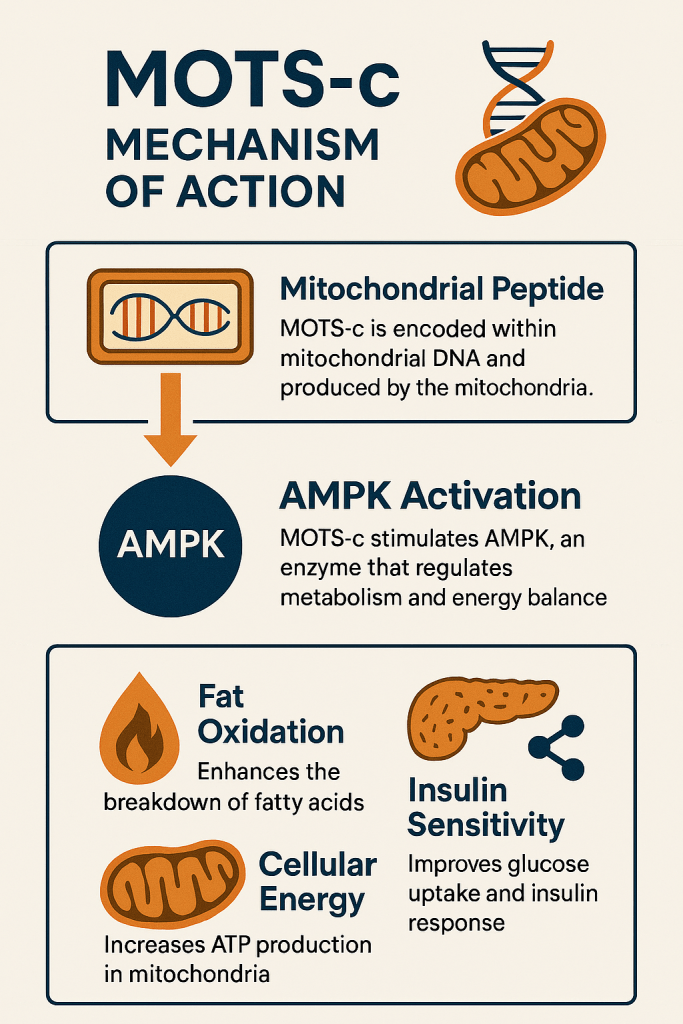
MOTS-c is a 16-amino acid mitochondrial-derived peptide that regulates cellular energy metabolism through AMPK pathway activation. AMPK pathway activation (defined as Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase) is basically when cells monitor their own energy status. Once activated, AMPK initiates a metabolic shift, promoting energy generation and halting energy consumption. It influences carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism throughout the body. The overall function of MOTS-C is to enhance glucose uptake, fat oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis, and cellular stress resilience. The result? Enhanced fat burning, improved insulin sensitivity, and greater energy efficiency throughout the body!
🌟 Benefits of MOTS-C
| Category | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Metabolic Health | Improves insulin sensitivity, glucose regulation, and metabolic flexibility |
| Fat Loss | Promotes fat oxidation, reduces adipose inflammation, and prevents diet-induced obesity |
| Energy & Performance | Enhances endurance, spares glycogen during exercise, and boosts ATP production |
| Longevity | Activates stress resilience pathways (FoxO), supports mitophagy, and reduces oxidative damage |
| Muscle Recovery | Improves mitochondrial efficiency and reduces muscle fatigue |
| Cognitive Function | May protect against neurodegeneration via mitochondrial support |
⚠️ Side Effects & Risks
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Injection Site Reactions | Redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site (common with subcutaneous peptides) |
| Metabolic Risks | Potential for hypoglycemia due to excessive AMPK activation, especially in sensitive individuals |
| Muscle Wasting | High doses may suppress mTOR, leading to muscle atrophy or impaired recovery |
| Cardiovascular Effects | Some animal studies show elevated blood pressure with prolonged use |
| Gastrointestinal Issues | Nausea, bloating, or altered bowel habits in some cases |
| Neurological Impact | Rare reports of dizziness or headaches; long-term effects unknown |
💉 Dosing Protocols
There are many different ways to dose MOTS-C and numerous studies have concluded that for the most part their isn’t really a wrong way. As a precaution, you should always start with what you deem a smaller dose to ensure no negative side effects before diving head on into larger and more frequent dosages.
| Goal | Dosage | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Use | 5–10 mg | 1x daily | 4–6 weeks |
| Metabolic Reset | 5 mg | Every 5 days | 4 doses over 20 days |
| Performance Boost | 10–20 mg | 3x/week | 4–10 weeks |
| Longevity Support | 10 mg | Weekly | Up to 10 weeks/year |
| Research Use | 0.5–1.0 mg/kg | Variable | As per protocol |
Administration: Subcutaneous injection, typically into the abdomen. Reconstitution with bacteriostatic water is required.
One scientific study highlights the promising usage of this peptide, and more information can be read online: HERE

Leave a comment