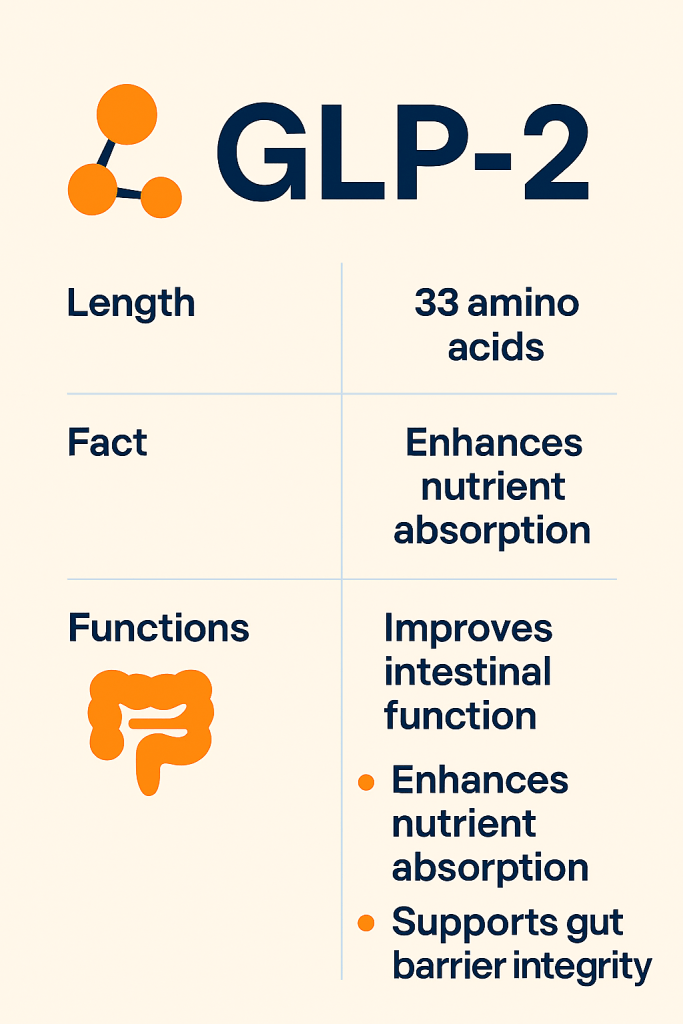
GLP-2 stands for Glucagon-like peptide-2 and is a hormone produced primarily by specialized L-cells in the small and large intestines. Its release is naturally triggered by the presence of nutrients in the gut after a meal. GLP-2 peptides get their name for being dual action. GLP-2s are what are known as both a gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) analog and a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Therefore, GLP-2s do what GLP-1s accomplish with the added GIP factor, making them arguably “better” for health implications and weight loss.
Synthetic versions of GLP-2, known as agonists, are used medicinally to manage conditions affecting gut function. These agonists are designed to be more resistant to degradation in the body, allowing for a longer-lasting effect compared to naturally produced GLP-2s.
Specifically, these agonists have a profound effect on the body.
- Promotes the growth and repair of the intestinal lining – GLP-2s increase the multiplication of intestinal epithelial cells and reduce apoptosis in these cells. Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. It is a normal and essential mechanism that helps eliminate damaged or unnecessary cells. This action helps maintain a healthy gut barrier.
- Improves nutrient absorption – GLP-2s increase the surface area of the intestinal lining, which is lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi. GLP-2 enhances villous height and crypt depth, leading to a more efficient uptake of nutrients.
- Strengthens the gut barrier – GLP-2s reduce gut barrier permeability. A strong barrier prevents harmful bacteria and toxins from leaking from the gut into the bloodstream, thereby supporting overall immune health.
- Slows down gastrointestinal motility – GLP-2s allow more time for nutrient absorption and helping reduce symptoms like diarrhea. It also helps reduce inflammation within the digestive tract by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines and promoting anti-inflammatory cytokines. Cytokines are a broad category of proteins that are produced by various cells in the body, particularly immune cells. They function as molecular messengers, facilitating communication between cells and regulating numerous biological processes, including immune responses, inflammation, and cell growth. Cytokines help coordinate the body’s defense against infections and diseases by signaling immune cells to respond to pathogens or injury.
What GLP-2 Medications are currently on the market?
Tirzepitide is the generic name for common GLP-2 medications such as Mounjaro and Zepbound. These medications are primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, and can assist with obesity management. They’ve also become increasingly popular for their effectiveness in managing blood sugar and reducing appetite, thus leading to significant weight loss. They are FDA approved.
What are the side effects of Tirzepitide?
⚠️ Common Side Effects of GLP-2 Medications are very similar to GLP-1 medications:
- Nausea – The most frequently reported side effect, due to slowed digestion
- Vomiting – Often linked to overeating or rapid dose escalation
- Diarrhea – Can occur as the digestive system adjusts
- Constipation – Slowed gastric emptying may reduce bowel movements
- Stomach pain or bloating – Related to changes in gut motility
- Fatigue – May result from reduced calorie intake or metabolic shifts
- Appetite changes – Suppressed hunger is expected, can feel extreme
- Indigestion or reflux – Due to delayed stomach emptying
- Headache or dizziness – Occasionally reported during early use
- Injection site and allergic reactions – All injections, including tirzepatide, can cause injection site reactions.
Nausea is the most common tirzepatide side effect. In clinical trials, up to 18% of people taking Mounjaro for diabetes and up to 29% of those taking Zepbound for weight loss reported experiencing it. Vomiting is also possible, though it’s less common. These side effects tend to happen when you first start tirzepatide, or after raising your dose. It’s also more common if you’re taking higher doses.
🚨 Rare but Serious Side Effects
- Pancreatitis – Some people have reported pancreatitis (pancreas swelling) with tirzepatide. But more research is needed to confirm if this is due to the medication or a different cause. While rare, pancreatitis is considered a medical emergency. You’d likely need to be treated in a hospital if this happens. Symptoms of pancreatitis include severe stomach pain, vomiting, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). A fever and low blood pressure can also happen. If you notice these while taking tirzepatide, seek emergency medical care.
- Gallbladder Disease – Gallbladder disease, including gallstones and cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation), can happen with tirzepatide. This side effect is very rare. But it can be painful and requires treatment. Weight loss from any cause can raise the risk of gallstones.
- Kidney Damage – Research suggests that tirzepatide may help protect your kidneys when taken long-term, but sudden kidney damage is also a possible tirzepatide side effect. This is typically a concern if you experienced severe vomiting or diarrhea that led to dehydration. Managing the more common stomach-related side effects can help prevent acute kidney damage. But you should also go for any regular blood tests your healthcare provider recommends.
- Thyroid Tumors – Mounjaro and Zepbound both have a boxed warning (the FDA’s strictest warning) about thyroid C-cell tumors. In animal studies, tirzepatide led to the development of these tumors. However, human studies haven’t confirmed this risk.
💡 Tips for Managing Side Effects
To help prevent or lessen nausea and vomiting, your healthcare provider will start you on a low dose of Mounjaro or Zepbound. They’ll slowly raise it over a period of several weeks. If you do experience these side effects, they should get better or go away over time.
Eating smaller meals and avoiding fatty foods can help limit nausea and vomiting as your body adjusts to tirzepatide. You can also ask your healthcare provider about over-the-counter (OTC) nausea medications.
If you experience severe or persistent nausea and vomiting, let your healthcare provider know. These aren’t typical and could be symptoms of more serious tirzepatide side effects, like pancreatitis.

Leave a comment